In this post, we present the work entirely accessible at link: Bézier Curves Based Novel Calibration Technique of Beamformers in IEEE 802.11 WLAN Networks, about a new way of doing beamforming in the wlan unified (WLC-based) network. Let’s recall that beamforming is the mean by which an access point (AP) concentrate the electromagnetic energy toward a client (WD or Wireless Device) to augment to accuracy of this transmission and efficiency among other benefits such as to reduce the amount of interference in such dense networks…
What this work about
The work argues that IEEE 802.11 WLAN networks face challenges for end-to-end service performance concerning new mobility applications: real-time interactive communications, analytics and business intelligence. In dense indoor deployments, co-channel interference is a major issue.
Deep dive in beamforming
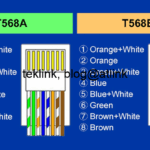
One of Radio Resource Management (RRM) techniques that is used to tackle this issue and maximize transmit opportunity is beamforming. From a signal processing perspective, the related-work concentrates on array elements’ signal weighting and phase shifting to achieve the desired angle of radiation, direction of arrival and gain. This work presents a novel beamformer’s calibration technique that enhances related-work results in the context of indoor WLAN network with a considerably lessened processing time and an augmented transmission quality.
A new CAGD-based beamforning technique
The work proposed solution model approach is based on concepts from Computed Aided Graphical Design (CAGD) especially Bézier curves, and takes advantage of now-a-day WLAN networks design and deployment characteristics.
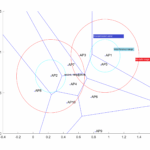
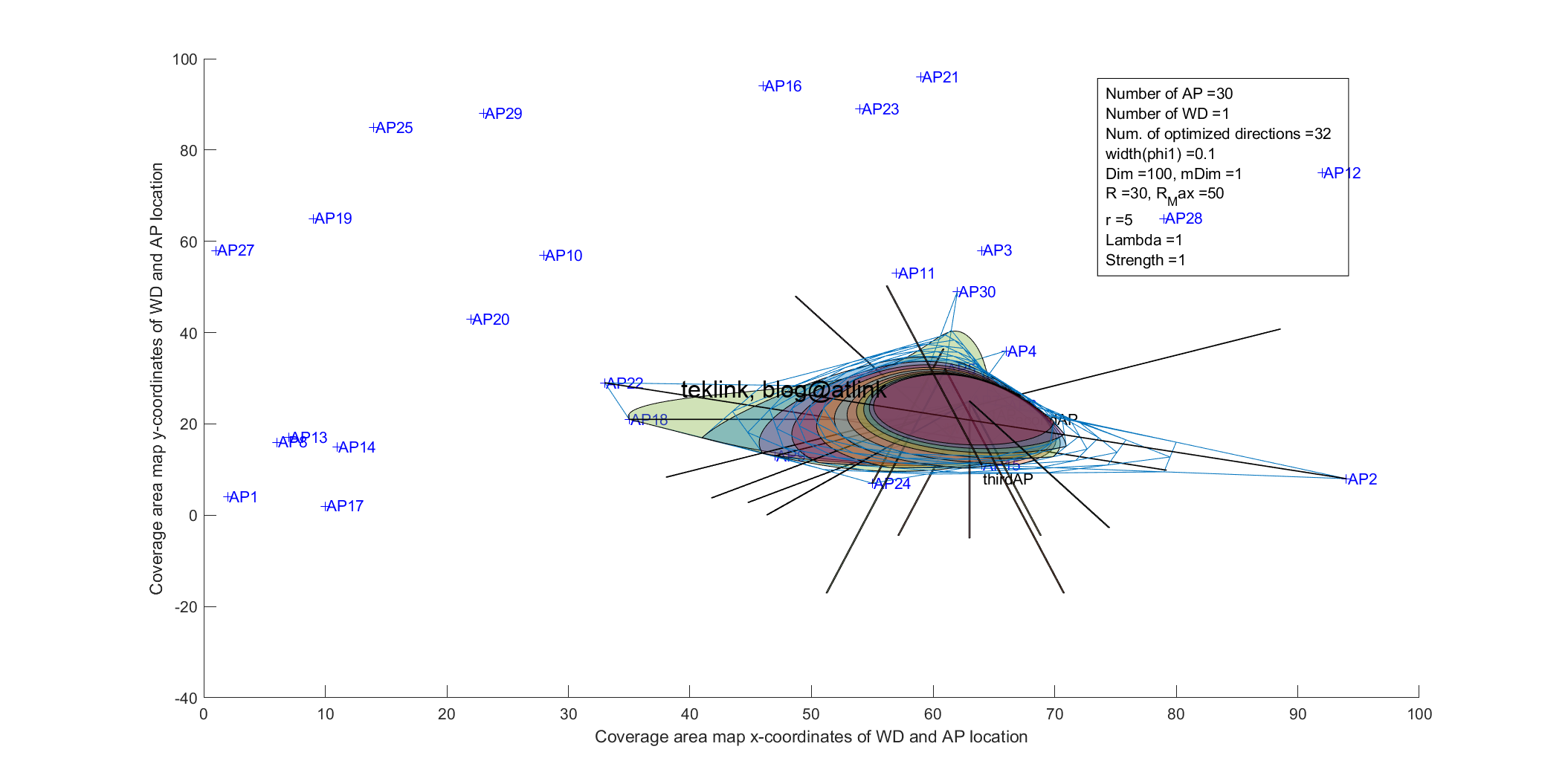
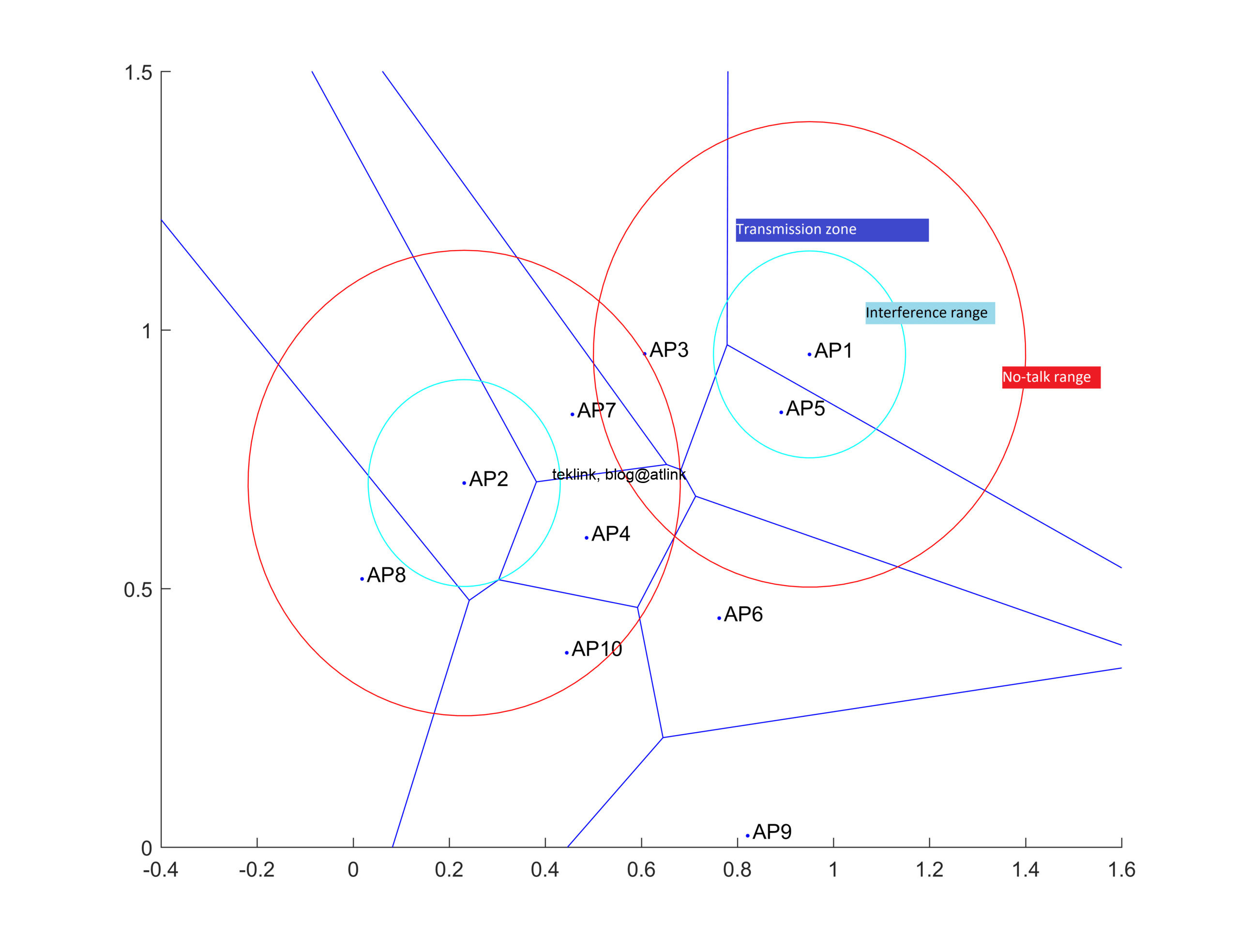
The figure shown next explains the basic idea behind this improvement.
This is a different approach to beamformer calibration in the context of indoor controlled-based (WLC-based) Wlan networks. The idea here is to evaluated the impact of the outer radio environment on a transmission instead of measuring at source on target the accuracy of this transmission and characteristics.
As a summary
The work concludes that in comparison with related-work, the study presented a new and scalable method to perform beamformer calibration at source. Some motivations behind it are: simple receiver design, lessened interaction with receivers, and high implementation costs of near or far field tests. In addition to these design aspects, the solution is demonstrated intrinsically adaptative to changes that are inherent to indoor dense WLAN networks. The solution’s Pseudo-AP enhancement allowed also the controller to decide on which AP to transmit and corresponding beamforming parameters. The remarkable benefit of this was to maximize the beamforming opportunity and at the same time prevent it from impacting the overall network operation.