In this post, we present the work fully available under this link: ML-Optimized Beam-based Radio Coverage Processing in IEEE 802.11 WLAN Networks, about radio coverage processing in wlan and its optimization using machine learning (ML).
Why dynamic RRM is important
Dynamic Radio Resource Management (RRM) is a major building block of Wireless LAN Controllers (WLC) function in WLAN networks. In a dense and frequently changing WLANs, it maximizes Wireless Devices (WD) opportunity to transmit and guarantees conformance to the design Service Level Agreement (SLA).
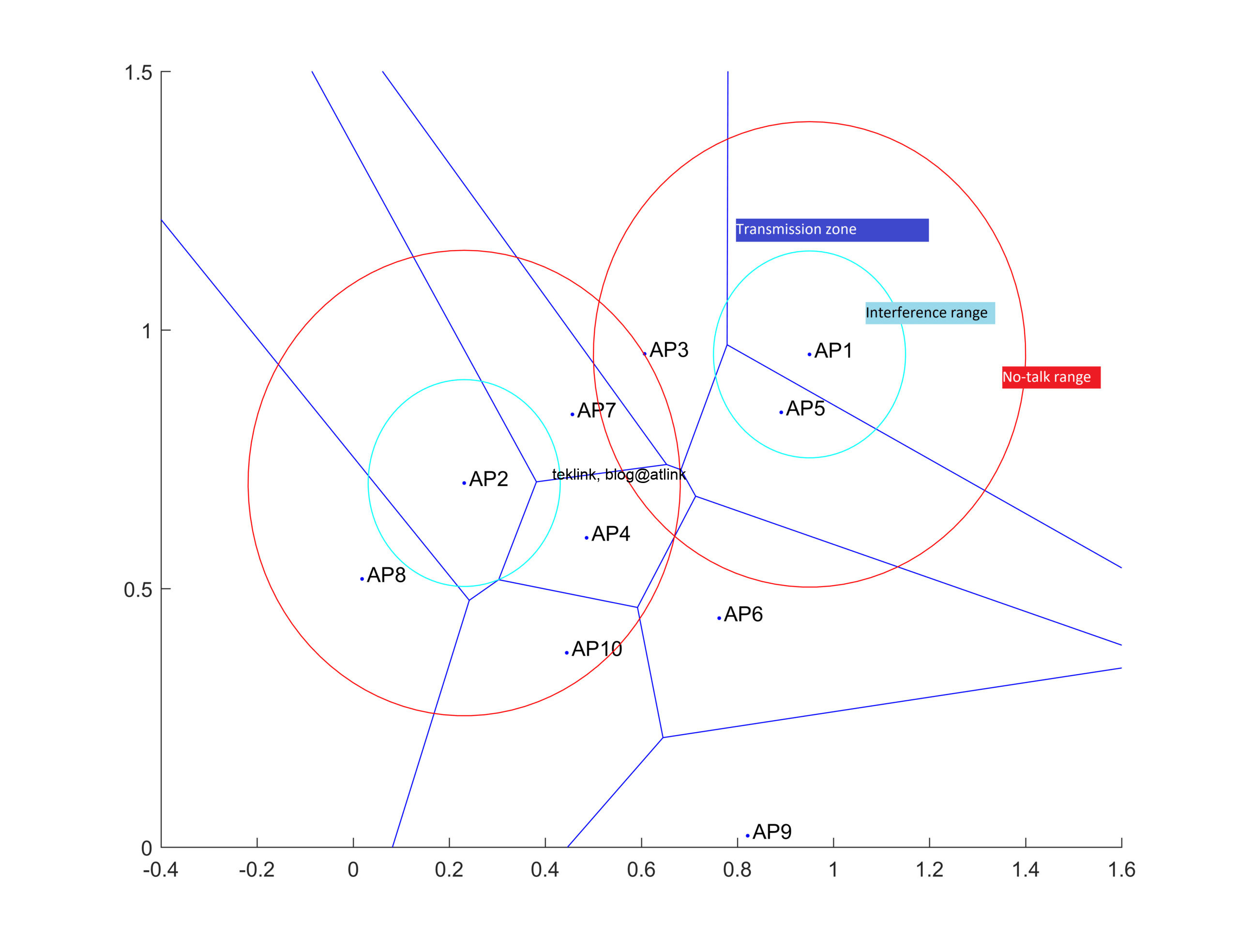
RRM in a WLC-based Wlan network
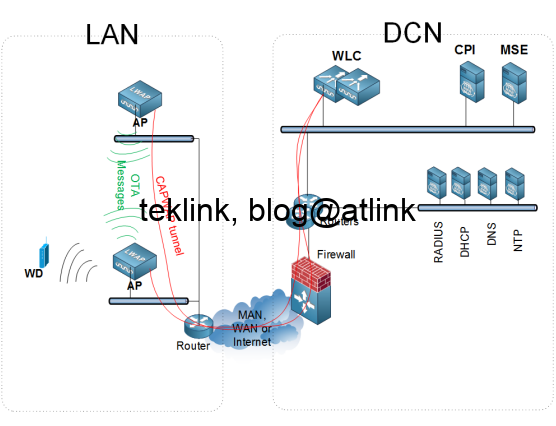
To achieve this performance, a WLC processes and applies a network-wide optimized radio plan based on data from access points (AP) and upper-layer application services. The next figure shows an example of unified wlan architecture aimed at supporting RRM operation and processings.
Processing the coverage
This coverage processing requires a “realistic” modelization approach of the radio environment and a quick adaptation to frequent changes. In this paper, the author builds on a Beam-based approach to radio coverage modelization. The work proposes a new Machine Learning Regression (MLR)-based optimization and compare it to the NURBS-based solution performance, as an out of path alternative: instead of analytically calculate the coverage we rely on the environmental variables to predict them…
A solution to optimize coverage map processing
The work shows that both solutions have very comparable processing times. Nevertheless, the MLR-based solution represents a more significant prediction accuracy enhancement than its alternative. The next figure shows an example of heatmap processing.
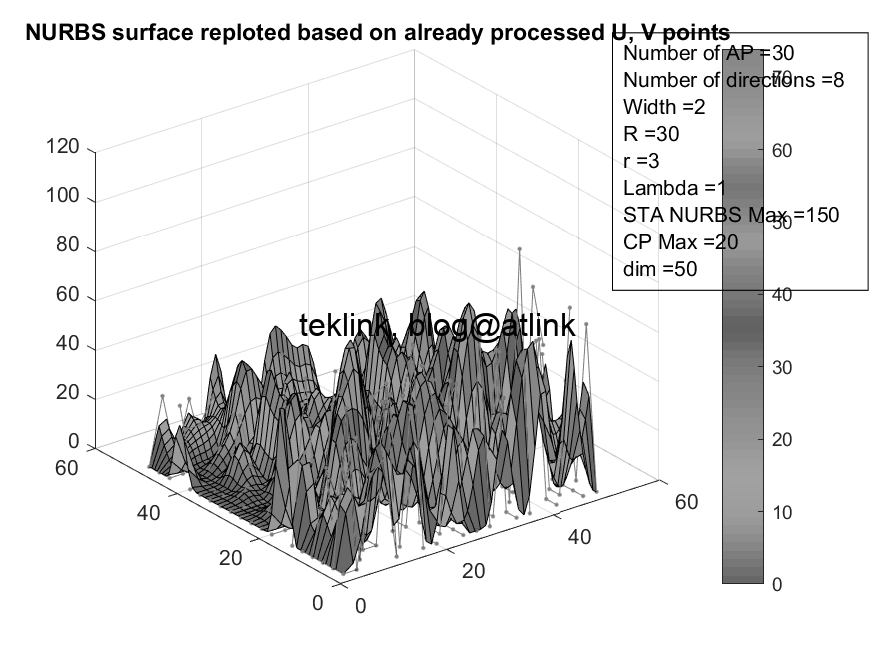
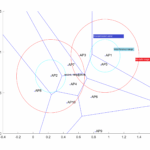
The NURBS based processing outputs the results in the next heatmap
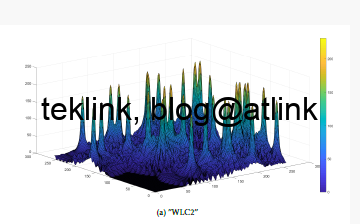
The MLR-based dRRM processing outputs the heatmap in the next figure that is very comparable the the first one generated by NURB-based dRRM