RIPv2…
Instead of using static routes, we advertise route Rt1 in RIP.
Changing the administrative distance of RIP routes in R4 is more coherent (makes sense) than the precedent case (using static route), in fact:
- Router R4 would prefer RIP-synchronized BGP routes if they have a better administrative distance;
- but deleting RIP route would cause BGP routes to get non synchronized in Loc-RIB;
- what is beautiful is that the corresponding paths get deleted also from RIB… forever!
let’s check with an OSPF route
In a normal situation, how a routing information bloc, included in the description of an OSPF route installed in RIB, would differ from the corresponding route information in Loc-RIB? a part from the prefix, subnet, mask, via interface, information, the router-id is shared between both RIB and Loc-RIB route descriptions but in the first case it corresponds the the advertising peer (R1) OSPF router-id and in the second case to the BGP router-id of the same router (R1)…
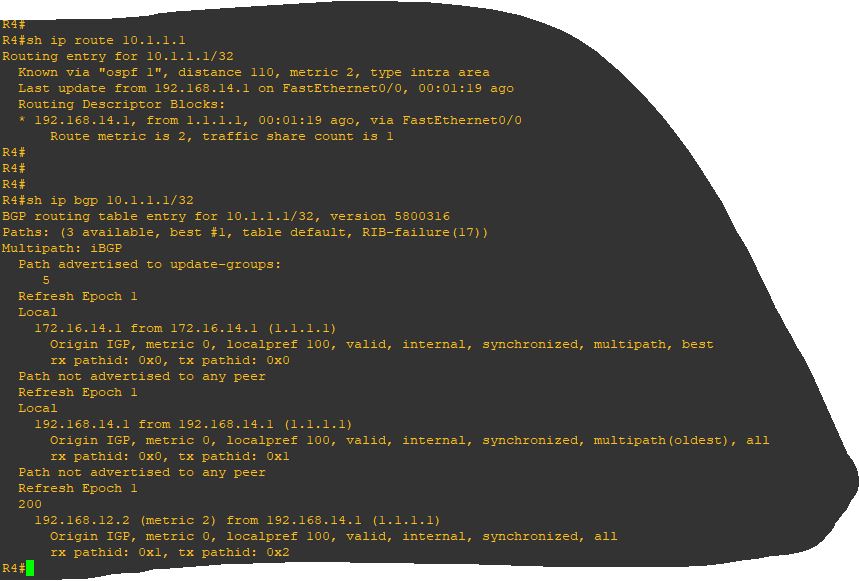
We’ve got a chance to have both router-id the same. The next figure shows that Rt1 is synchronized
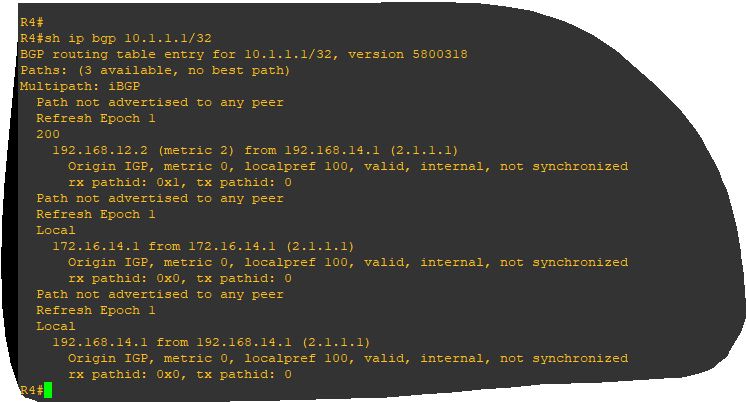
In case R1 BGP router-id is different from R1 OSPF router-id, Rt1 gets not synchronized in R4.
Let’s test the administrative distance…
We check that:
- similiarily to static route case, the BGP routes are not deleted from the routing table!
- the routes are not synchronized in Loc-RIB nor advertised to peers (R5).
- Using a different subnet mask prevents the route from getting synchronized, installed in RIB and advertised to peers.
what about EIGRP?
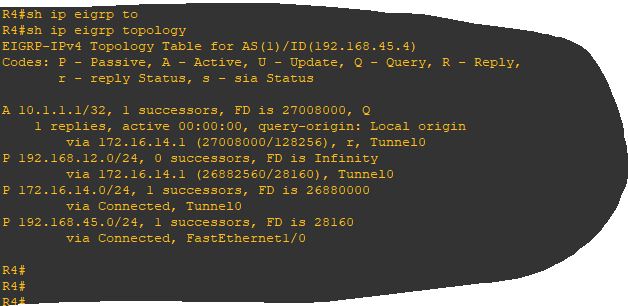
Testing administrative distance and subnet match results are the same as RIP but we observe in EIGRP topolgy that the corresponding route is marked as Active and the router is actively querying the neighbors for an alternative successor.
A debug on ip routing shows that:
- the process add the EIGRP route first,
- the route in the Loc-RIB get marked as synchronized,
- having a better administrative distance, BGP route is installed in RIB,
- the process deletes the EIGRP route and EIGRP put the corresponding route in topology into active state,
- but BGP detects that EIGRP route has disappeared and put Rt1 into a non synchronized state,
- BGP paths get deleted from the RIB,
- the loop starts again from the beginning…
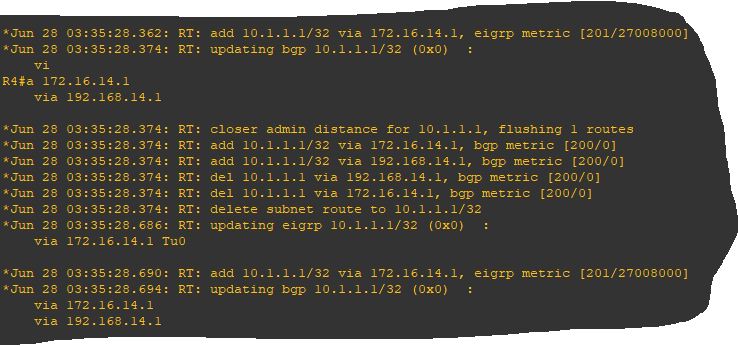
This is not resource efficient…
Conclusion
BGP IGP synchronization concerns only I-BGP peerings.
A matching route from an IGP or static sources should have the same prefix and subnet as the BGP route. The nexthop does not match necessarily and might be any resolvable address (direct or intermediate address).