This post is a part of series of posts about RIP dynamic routing protocol. Here we deepen our understanding on how RIP protocol advertises learnt RIP routes. A simple case is where a route is in the m...
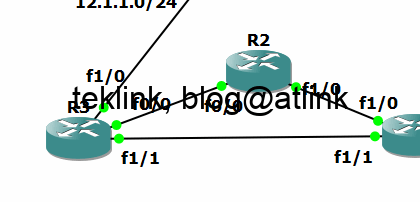
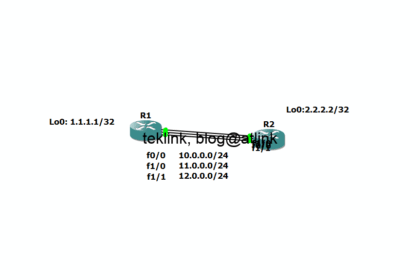
RIP is Routing Information Protocol, one of the IGP or Interior Gateway Porotocols called also a vector-based routing protocol in contrast with link-state, hybrid or path-based protocols. The function...
This post is part of a series of blogs about RIP functionning from the basic to the more complex operation. Let’s recall that RIP stands for Routing Information Protocol and is an IGP (Interior ...
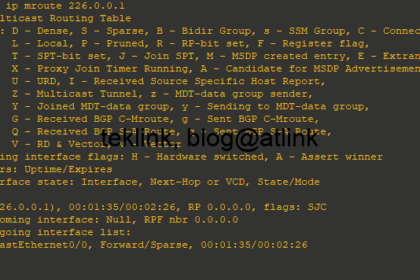
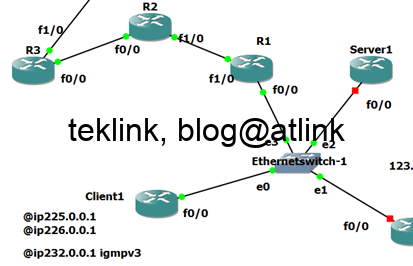
In this post we review a basic multicast routing operation, step by step using output from routers console and traffic packet capture (using wireshark). Introduction This blog is a part of a serie of ...
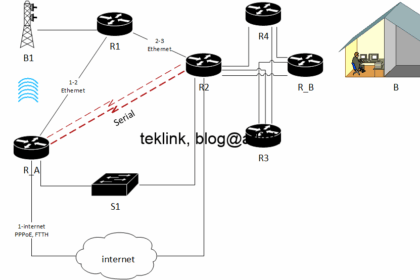
Let’s discuss in this blog, the operation of routing using a simple network example: a home network. Introduction The person in A wants to join its colleagues in location B through the network t...
Dans ce blog, nous discuterons du SD-WAN pour essayer de comprendre son enjeu et avantage pour l’entreprise. Nous commençons par explorer l’offre du marché, définir la technologie et son p...