This blog is a part of series of posts about EIGRP routing protocol. Let’s recall that EIGRP is one of the so called IGP routing protocols. IGP stands for interior routing protocols as opposed to EGP or exterior routing protocols. In addition EIGRP is a hybrid as it borrows some similiarities to distance-vector and link-state type of routing processing by protocols such as: RIP and OSPF.
In this post we explore how DUAL (diffusing update algorithm) route FSM (finite state machine) works. DUAL is the way EIGRP helps keep routing information consistent among all routers belonging to the same domain.
DUAL route FSM into play
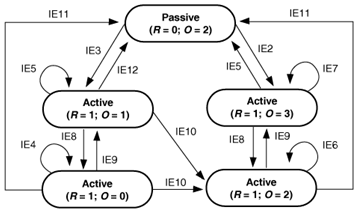
An interesting case of how DUAL route FSM operates is presented next. We see in the next figure that the FSM is a 5 states: one passive and four active states, and almost 12 events kind of pseudo code or algorithm. the R and O are reply status and origin of a route.
First let’s note that an EIGRP router send a Query to its neighbor to find a better route to a destination that has passed from Passive (working state) to Active (not working any more) state; that is actively searching for a new feasible route to a destination that no more satisfies the Feasibility Condition (to be installed in the effective routing table or validated for adverstisment to other neighbors).
at first
After EIGRP packet generic input processing (to validate the packet), a router that receives a Query message checks if the corresponding route is Passive (working state) or Active (in its database in a non working, routing state).
router is passive for the route
If router is Passive for this route and a neighbor has reported (kind of reply to a query) an unreachable metric, by means of 0xffffffff put in the field corresponding to the cumulative Delay part of Metric, a reply is sent immediately to this neighbor hinting him to consider rather information contained in Reply message (with its information).
If metric is not UNreachable, then the router considers checking FC (the feasibility) condition by adding Query information to its computation. If FC condition is still met, it replies to its neighbor with this received information (meaning that the router is on the best route from the neighbor to the destination).
router is active for the route
If Not (the router is not on the best route), it put its own prefix in Active (not working or routing) state. Further, it sends a Reply to its neighbor if he does not correspond to the current Successor (kind of a split horizon rule). If the Query was received from the Successor (representing the best route), only the Query Origin code is set to 3 in FSM (event IE2). Otherwise, it is set to 1 (FSM event IE3).
If router is Active for this route upon reception of the Query message, then it changes the current route Query Origin code to corresond to 2 (FSM event IE10), if the message was received from the Successor. Otherwise, it sends a Reply to this neighbor.
in general
It is interesting to see that whenever the router considers it has a better route to a destination it replies to its neighbor. If it considers that it may not have the best route, route is passed to Active state and it replies back to the neighbor provided that it’s not the current route Successor (the one presenting the best route cost calculation to the target network).


One Comment
test