In this post, we present the work fully available at this link: A NURBS-optimized dRRM solution in a mono-channel condition for IEEE 802.11 entreprise Wlan networks, about dynamic RRM (Radio Resource Management) and especially on a NURBS optimized solution of RRM. NURBS relates to Non-Uniformal Rational B-Splines surfaces concepts usually known in CAGD (Conception Aided Graphical Design).
What is dynamic RRM
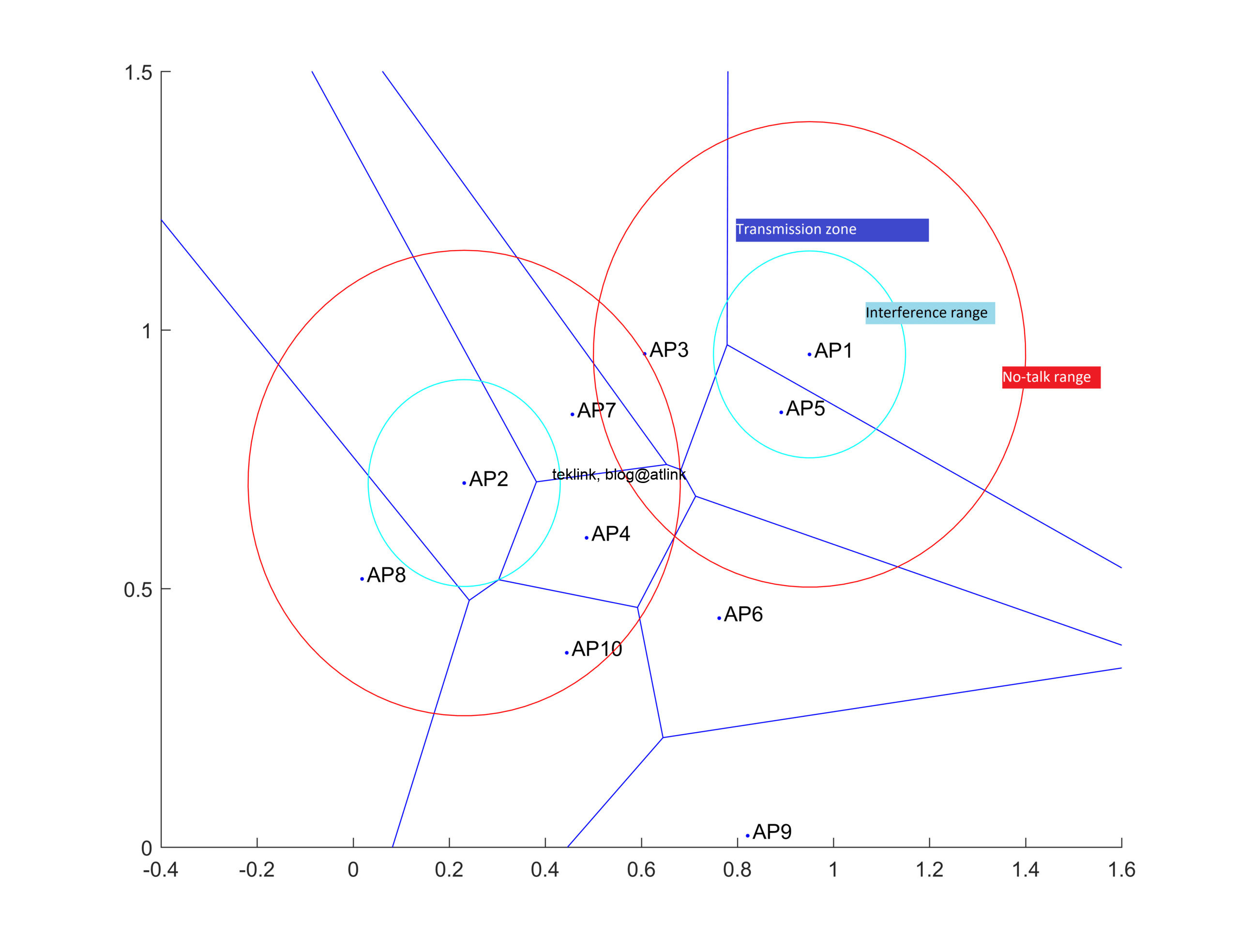
Dynamic Radio Resource Management, RRM, is an essential design block in the functional architecture of any Wifi controller in IEEE 802.11 indoor dense enterprise Wlans. That in a mono-channel condition, it helps tackle co-channel interference problem and enrich end-to-end Wifi clients experience.
A dRRM solution
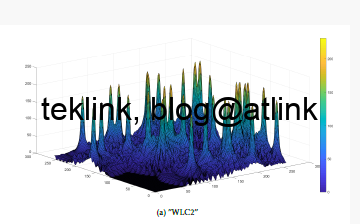
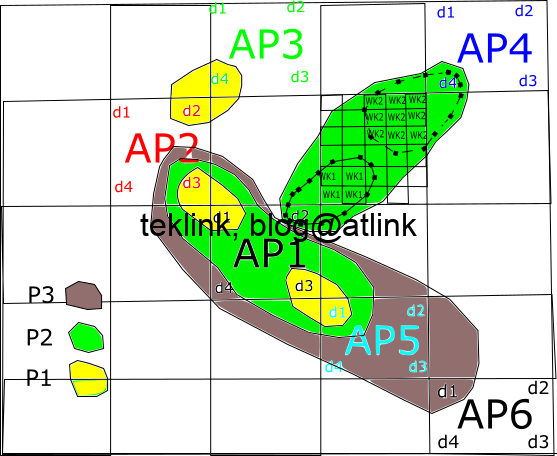
In this work is present a novel dRRM solution: WLCx. Its performance is demonstrated over related-work and vendor approaches. The solution is built on a novel and realistic per-Beam coverage representation approach already discussed in previous work. Unlike the other RRM solutions, WLCx is dynamic: even the calculation system parameters are processed which comes at price in terms of processing time.
The idea behind our solution
To overcome this limitation, the work constructed and implemented a NURBS surface-based optimization to the basic (initial) RRM solution. The work demonstrated that the NURBS optimized WLCx, N-WLCx, solution achieves almost 92.58% time reduction in comparison with basic WLCx. Furthermore, the optimization could easily be extended to enhance others, vendors and research, RRM solutions. The idea is shown in the next figure: